MAO Quick Start
-
Choose the Update Economics command (Task Pane >> MFO group) to vary prices and/or costs over time, define blended products as processing methods or use economic parameters that differ from the Economic Model parameters.
Check Use these settings check box on the Options page, to store MAO settings and use them for optimization. Y
Note : You can revert to Economic Model settings anytime by checking Use Economic Model.
-
To define blended products, say STD and TT2:
-
Choose the Update Economics command (Optimization control bar, Allocation & Flow section).
-
Add STD and TT2 “processing methods” to all rock types you want to include in the products; edit the method parameters as required.
-
Delete the original processing methods unless there is a reason to keep them.
-
Save your changes; the product quality requirements are set in MAO settings.
-
-
Define grade classes (on the MAO-MFO OptimizationSettings dialog's Mine Inputs screen):
-
Grade classes are defined separately for each ore (raw material) type listed on top of the page.
-
Select grade (quality) classification criterion that best suits your project.
Note: For MFO (cutoff grade optimization), Grade of selected element option is best if you have just one product; in multi-product projects Total value of all products is usually preferable.
-
Choose the number of grade classes. This number includes the class below the minimum grade and the class above the maximum grade.
-
Explicit rules allows you to define each class by a logical formula type rule. A formula is a function of elements; an ore (raw material) parcel will be included in the corresponding class if, and only if, the function yields nonzero value. The number of grade classes equals the number of rules plus one for material that fails to satisfy all rules.
-
The grade class parameters for different material types are independent from one another.
-
-
Optionally, define stockpiles (MAO-MFO OptimizationSettings dialog - Stockpiles IandStockpiles II screens):
-
Add the stockpile name to the list.
-
Select the material type that will go to this stockpile.
-
Set the storage capacity, rehandling cost, product recovery adjustment, maximum reclaim rates (can vary in time and can be zero).
-
If it is a pre-existing stockpile, define its content.
-
Click Apply to save the parameters for this stockpile.
-
Keep adding other stockpiles. Any material type may have zero, one or more stockpiles.
-
Note that grade requirements for stockpiles, if any, are set as destinations quality targets on the Destinations screen.
-
-
Optionally, define external material sources (MAO-MFO OptimizationSettings screen - Stockpiles II screen). The procedure is similar to defining stockpiles although the parameters are different.
-
Define Destination properties (MAO-MFO OptimizationSettings screen - Destinations screen). The destination list includes all processing methods (blended products) and stockpiles. Select a destination and:
-
Define the destination capacity per time period (usually a year). Note that you can define capacity for stockpiles as well as for processing methods:
-
Unlimited capacity: destination accepts unlimited material deliveries.
-
Deliver at or below the limit: no more than the stated limit per year.
-
Deliver exactly at the limit: destination requires deliveries exactly at the stated limit.
-
Define zero, one, or more quality targets for the destinations. The targets are rates and ratios of grades; target limits can change over time. Setting quality targets procedure is the same as for Scheduler targets or MAO global targets, except that the arguments of quality target expressions are element grades, not masses.
-
-
Optionally, define global targets:
-
Define variables to use in the target definitions. A variable can have one of three forms:
-
Input_Destination
-
Input_Destination_Element
-
Input_Destination_Product-R (R stands for recovered).
-
-
Define the targets in the usual way in terms of the above defined variables.
Note: All variables represent mass
-
-
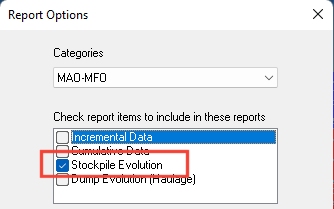
To display a Stockpile Evolution report, activate the Optimization ribbon and select Reports >> Options and select the Stockpile Evolution toggle under the MAO-MFO category, for example:
Related topics and activities